Patients suffering chronic pain are being denied treatment in low-income countries because of restrictive laws and concerns about opioid addiction, which have been fueled by the crisis engulfing the US.
Palliative doctors, who say there is a huge unmet need for pain-relief drugs in poorer countries, have called for laws to be relaxed and for the stigma around opioids to be addressed.
Only 17% of the morphine produced worldwide in 2020 for medical purposes was consumed in low- and middle-income countries, despite them being home to close to 83% of the global population, according to the latest figures from the International Narcotics Control Board, which monitors drug use. It said the imbalance in usage has barely changed in 20 years.
As of 2017 lancet commission study found that Haiti received an annual average of just 5mg of morphine-equivalent opioids for each patient requiring palliative care – 0.8% of what is needed – compared with the US, which received 55,000mg for each patient, more than 3,000% of the required amount.
“What I witness myself every day are people who have been on disease-specific treatment going through pain and suffering through weeks, months or years,” said Dr MR Rajagopal, the chairman of Pallium India, a palliative care charity based in Kerala. “At least 96% of them in my country are eventually denied pain relief. I have seen several people with scars around the neck from attempting to kill themselves by hanging.”
Rajagopal said very few patients reached palliative care clinics where they could finally access pain-relief drugs suitable for their conditions and that doctors were often scared to prescribe them.
He said draconian laws grew out of a 1961 international treaty that emphasized the control of opioids in order to stop drug abuse. The resulting global “war on drugs”, which effectively criminalized production and supply even in medical contexts, led hospitals and pharmacies to stop stocking opioids. The result, he said, was that India’s use of opioids dropped from 600kg a year in 1985 to 17kg in 1997.
NCDs are simply that; Unlike, say, a virus, you can’t catch them. Instead, they are caused by a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioral factors. The main types are cancers, chronic respiratory illnesses, diabetes and cardiovascular disease – heart attacks and stroke. Approximately 80% are preventable, and all are on the rise, spreading inexorably around the world as aging populations and lifestyles pushed by economic growth and urbanization make being unhealthy a global phenomenon.
NCDs, once seen as illnesses of the wealthy, now have a grip on the poor. Disease, disability and death are perfectly designed to create and widen inequality – and being poor makes it less likely you will be accurately diagnosed or treated.
Investment in tackling these common and chronic conditions that kill 71% of us is incredibly low, while the cost to families, economies and communities is staggeringly high.
In low-income countries NCDs – typically slow and debilitating illnesses – are seeing a fraction of the money needed being invested or donated. Attention remains focused on the threats from communicable diseases, yet cancer death rates have long sped past the death toll from malaria, TB and HIV/Aids combined.
‘A common condition’ is a new Guardian series reporting on NCDs in the developing world: their prevalence, the solutions, the causes and consequences, telling the stories of people living with these illnesses.
Tracy McVeigh, editor
“,”credit”:””,”pillar”:0}”>
QuickGuide
A common condition
Show
The human toll of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) is huge and rising. These illnesses end the lives of approximately 41 million of the 56 million people who die every year – and three quarters of them are in the developing world.
NCDs are simply that; Unlike, say, a virus, you can’t catch them. Instead, they are caused by a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioral factors. The main types are cancers, chronic respiratory illnesses, diabetes and cardiovascular disease – heart attacks and stroke. Approximately 80% are preventable, and all are on the rise, spreading inexorably around the world as aging populations and lifestyles pushed by economic growth and urbanization make being unhealthy a global phenomenon.
NCDs, once seen as illnesses of the wealthy, now have a grip on the poor. Disease, disability and death are perfectly designed to create and widen inequality – and being poor makes it less likely you will be accurately diagnosed or treated.
Investment in tackling these common and chronic conditions that kill 71% of us is incredibly low, while the cost to families, economies and communities is staggeringly high.
In low-income countries NCDs – typically slow and debilitating illnesses – are seeing a fraction of the money needed being invested or donated. Attention remains focused on the threats from communicable diseases, yet cancer death rates have long sped past the death toll from malaria, TB and HIV/Aids combined.
‘A common condition’ is a new Guardian series reporting on NCDs in the developing world: their prevalence, the solutions, the causes and consequences, telling the stories of people living with these illnesses.
Tracy McVeigh, editor
He said advocacy efforts had helped relax regulations in Kerala and other parts of India, but that still only 350kg of opioids a year were being consumed, whereas he estimated that 30,000kg were now needed.
Gary Rodin, who is the director of the Toronto-based Global Institute of Psychosocial, Palliative and End-of-Life Care and has carried out research into habits of prescribing opioidssaid the increase in rates of diseases such as cancer and diabetes in low- and middle-income countries demanded greater emphasis on relieving pain and psychological distress.
“Maybe 100 years ago that would have been a large part of medicine. As medicine has become more specialized and technologised, people have paid more attention to Cat scans and MRIs and blood tests than they have to the suffering of the patient. They haven’t asked enough about the suffering,” he said.
That has resulted in more aggressive chemotherapy treatment, Rodin said, even at stages when it is unlikely to work and when the body struggles to handle it.
“Suicide rates are very high in advanced disease. Psychological distress is very common; family distress is very common. There are lots of approaches which we have evidence will help, but we don’t do nearly enough to support that.”
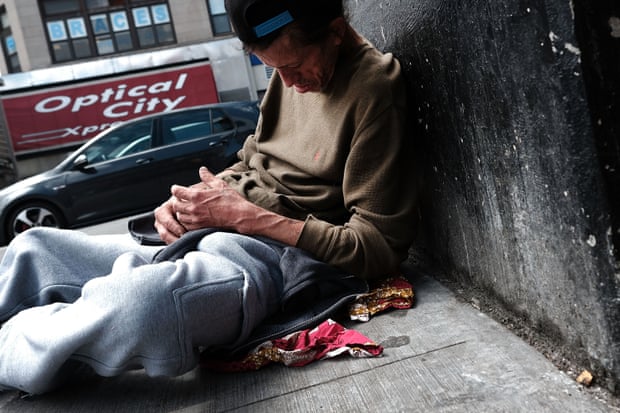
Palliative care can be a cheaper way to ease the suffering of terminally ill patients and could be made more available by relaxing laws and training healthcare workers to administer painkillers and ease psychological distress, Rodin said.
Julia Downing, the chief executive of the International Children’s Palliative Care Network, said neglecting a patient’s pain can have a significant impact on their quality of life.
“The implications are quite broad … If they’re unable to work, the family will become poorer and poorer, and then they can’t pay for school fees, so the children can’t go to school. The impact of having people whose pain is not controlled goes far beyond just that individual themselves,” she said.
Rajagopal said the US opioid crisis has affected how opioids are viewed globally, fueling fears among doctors that patients who are prescribed them will become addicted. However, he said, addiction in the US was specific to that context, where pharmaceutical companies aggressively marketed opioids.

“Pain is not visible. It happens in hospital beds or patients’ rooms and is not visible to the world. Addiction, on the other hand, is very visible in headlines which quote the US epidemic and overdose deaths. No one talks about the western European success over decades; all the news is about the opioid crisis in the USA. This means that when we try to have discussions, our work becomes harder because many minds are primed against opioids,” said Rajagopal.
Downing said progress has been made in Uganda, India and Kenya but more needed to be done not just on legislation but also on training medical staff.
Zipporah Ali, a Kenyan palliative care doctor, said some progress has been made in her country to relax opioid laws.
“There was a time a patient came to me in so much pain with a neck tumor that was so swollen, he just wanted to die. But I started him on treatment with high doses of pain management and steroids. The next week in the hospital he came and grabbed me to say: ‘Thank you. I don’t want to die any more.’” said Ali. “We are not curing the disease, but it can make you comfortable.”
www.theguardian.com
George is Digismak’s reported cum editor with 13 years of experience in Journalism